Description:
Azure Active Directory (now Microsoft Entra ID) provides identity-based authentication and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) for managing access to Azure resources and services. Replacing traditional shared keys, usernames, or passwords with Entra ID identities significantly improves security by enabling centralized authentication, conditional access, MFA enforcement, and granular role assignments. Using Entra ID for client authentication ensures modern, secure, and auditable access patterns for Azure services such as Key Vault, Storage Accounts, SQL Database, and Azure Kubernetes Service.
Rationale:
Identity-based authentication greatly reduces the risks associated with shared credentials, static access keys, and connection strings. Azure RBAC offers least-privilege access control and improves auditability across services. Enabling Entra ID authentication ensures stronger security, better onboarding/offboarding, compliance enforcement, and alignment with Zero Trust and cloud governance best practices.
Impact:
Adopting AAD/Entra authentication increases security and reduces credential exposure but may require application updates to support identity-based access and may require additional configuration of roles and permissions.
Default Value:
Many Azure services default to using access keys or SQL logins unless Entra ID authentication is explicitly configured.
Pre-Requisites:
Microsoft Entra ID tenant
Appropriate Azure RBAC roles assigned (for example: Reader, Contributor, Key Vault Secrets User, Storage Blob Data Contributor)
Applications or services must support Entra ID authentication
Admin access to configure authentication settings
Test Plan:
Sign in to the Azure Portal at https://portal.azure.com
Search for and open the target resource (for example, Azure Cosmos DB)
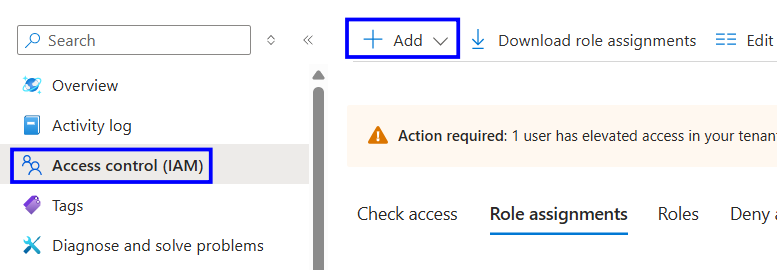
From the left menu, select Access control (IAM)
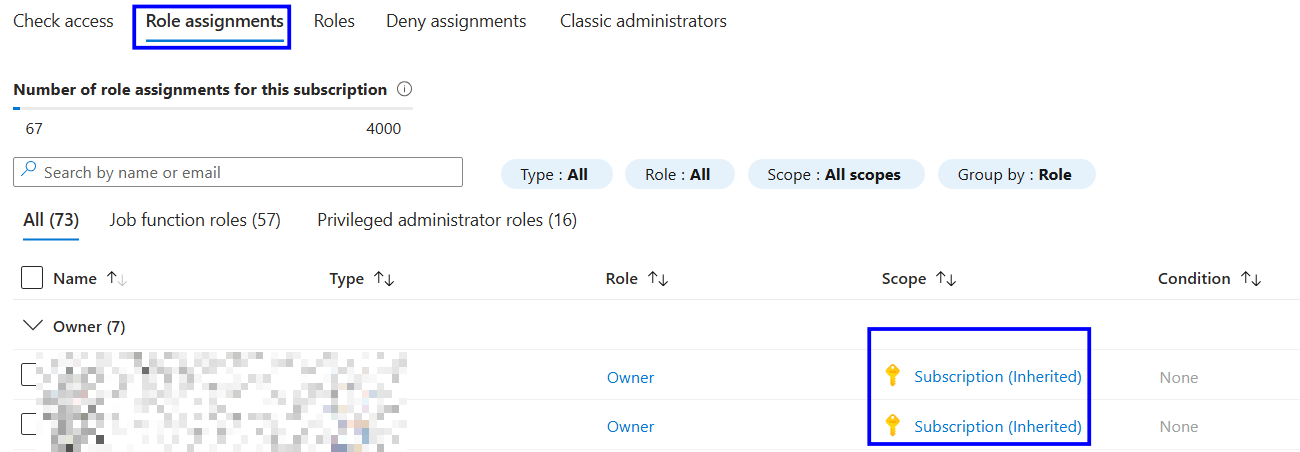
Open Role assignments
Verify users, groups, or managed identities are assigned Azure RBAC roles (such as Reader, Contributor, or Owner)
Confirm access is granted through Azure AD identities and not through account keys or connection strings
If RBAC-based access is not configured, follow the implementation steps
Implementation Steps:
Sign in to the Azure Portal
Open the target Azure resource
Select Access control (IAM)
Click Add, Add role assignment
Select an appropriate Azure built-in role (Owner, Contributor, Reader, or required role)
Assign the role to a user, group, or application from Microsoft Entra ID
Save the role assignment
Backout Plan:
Sign in to the Azure Portal
Open the target Azure resource
Select Access control (IAM)
Locate the role assignment
Remove the Azure RBAC role from the user, group, or application
Save the changes
Reference:
https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/role-based-access-control/overview
https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/key-vault/general/rbac-guide
https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/storage/common/storage-auth-aad